Introduction: Navigating Hair Loss Treatments in 2025
In the United States, androgenetic alopecia affects over 50 million men and 30 million women, according to the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD). As we enter 2025, the two FDA-approved gold standards for treatment—Minoxidil and Finasteride—continue to dominate discussions on hair regrowth. But with new studies emerging, many Americans are asking: Which one works faster? Does combining them yield better results? And what do the latest clinical trials say?
This comprehensive guide dives deep into the science, drawing from recent 2025 research published in journals like Frontiers in Medicine and the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology (JAAD). We'll compare mechanisms, timelines, efficacy, and side effects to help you make an informed decision. Whether you're a 30-something noticing a receding hairline or someone battling diffuse thinning, understanding these treatments can restore confidence and hair.
Internal link suggestion: Explore our top Minoxidil recommendations
Understanding Androgenetic Alopecia: The Root Cause of Hair Loss
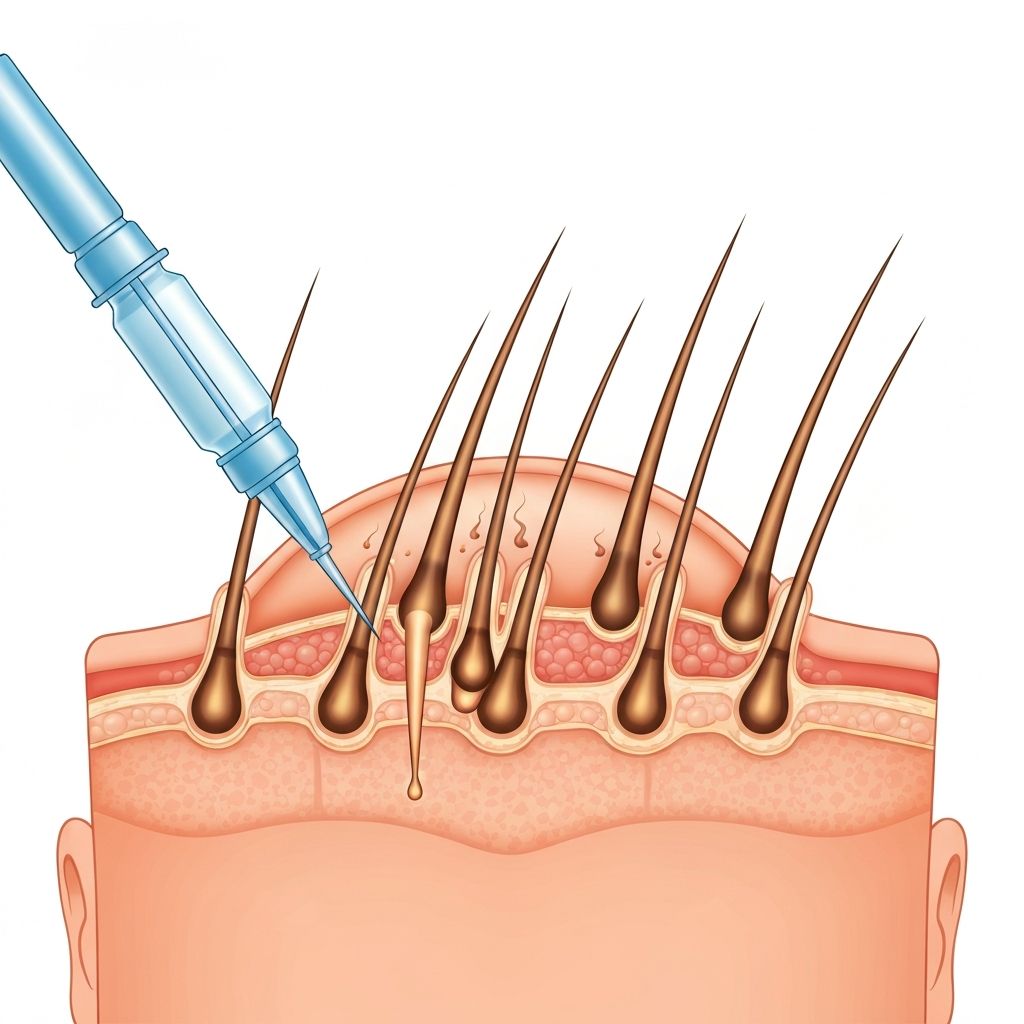
Androgenetic alopecia, often called male or female pattern baldness, stems from a genetic sensitivity to dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a hormone derived from testosterone. In men, it typically starts with a receding hairline and crown thinning; in women, it presents as widening parts or overall volume loss. The National Institutes of Health (NIH) estimates that by age 50, 50% of men and 40% of women in the US experience noticeable hair loss.
DHT shrinks hair follicles over time, shortening the growth phase (anagen) and prolonging the resting phase (telogen). Early intervention is key—treatments like Minoxidil and Finasteride aim to interrupt this cycle. According to Mayo Clinic guidelines, starting therapy before significant follicle miniaturization maximizes outcomes.
- Key Statistic: A 2025 NIH review found that untreated alopecia progresses in 85% of cases within five years.
- US Context: With rising telehealth access via platforms like the AAD's Find a Dermatologist tool, more Americans are seeking FDA-approved options early.
Internal link suggestion: Learn more about male pattern baldness causes
How Minoxidil Works: Boosting Blood Flow for Quicker Visible Changes
Minoxidil, available over-the-counter as Rogaine in 2% and 5% topical solutions or foam, was originally developed for hypertension. Its hair benefits were discovered serendipitously when patients reported unexpected growth. The FDA approved it for alopecia in 1988.
Mechanistically, Minoxidil is a vasodilator that widens blood vessels around follicles, increasing nutrient and oxygen delivery. It also prolongs the anagen phase and may stimulate prostaglandin pathways for growth. Unlike hormone blockers, it doesn't address DHT directly but promotes follicle activity regardless of cause—making it versatile for men and women.
Men's Rogaine 5% Minoxidil Foam
FDA-cleared 5% minoxidil foam clinically proven to regrow hair in men with hereditary hair loss.
A 2025 study in PubMed Central highlighted Minoxidil's role in reactivating dormant follicles, with 5% formulations showing 30-40% greater efficacy than 2% in men.
- Apply twice daily to a dry scalp.
- Massage gently for absorption.
- Expect initial shedding (telogen effluvium) in weeks 2-6 as old hairs make way for new.
Internal link suggestion: Minoxidil for female hair loss
How Finasteride Works: Targeting DHT for Long-Term Prevention
Finasteride, sold as Propecia, is a prescription oral 5-alpha reductase inhibitor approved by the FDA in 1997 for male pattern baldness. It blocks the conversion of testosterone to DHT, reducing scalp levels by up to 60-70%, per Harvard Health Publishing.
By lowering DHT, Finasteride halts follicle miniaturization and can reverse early thinning. It's highly targeted for androgenetic alopecia but not recommended for women of childbearing age due to teratogenic risks. A Cleveland Clinic overview notes it's most effective in the crown area.
DHT Blocker - Hair Growth Supplement for Genetic Thinning for Men & Women
Gluten-free vegetarian DHT blocker clinically developed to combat thinning hair caused by DHT.
Recent 2025 data from the British Journal of Dermatology emphasizes low-dose (0.25mg) topical versions to minimize systemic exposure.
- Dosage: 1mg daily for optimal results.
- Onset: Stabilizes loss in 3 months; regrowth peaks at 12 months.
- Monitoring: Annual PSA tests advised for men over 50.
Internal link suggestion: Debunking Finasteride myths
Speed of Results: Minoxidil vs. Finasteride Timeline Comparison
One of the most common questions from US patients is, "Which works faster?" Based on aggregated 2025 meta-analyses, Minoxidil often shows visible changes sooner due to its direct stimulation, while Finasteride excels in sustained prevention.
| Treatment | Initial Shedding | Noticeable Regrowth | Peak Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Minoxidil 5% | 2-6 weeks | 2-4 months | 6-12 months |
| Finasteride 1mg | Rare | 3-6 months | 12-24 months |
Per a GoodRx analysis, about 60% of Minoxidil users see thicker hair by month 3, versus 40% for Finasteride. However, Finasteride prevents further loss more reliably long-term. For faster results, Minoxidil edges out, but consistency is crucial—discontinuation reverses gains in 3-6 months for both.
Internal link suggestion: Your hair growth timeline guide
Efficacy Breakdown: What 2025 Studies Reveal
2025 has brought pivotal research affirming both treatments' value, with a tilt toward combinations. A Frontiers in Medicine systematic review (October 2025) compared topical Minoxidil-Finasteride mixes to monotherapies in 500+ men, finding the combo increased hair density by 28% more than Minoxidil alone and 15% over Finasteride.
Another JAAD study reported Finasteride's superiority for severe cases: 66% stabilization vs. 52% for Minoxidil. For women, Minoxidil remains first-line, per AAD guidelines, with off-label low-dose Finasteride under dermatologist supervision.
- Key Finding: Dutasteride (stronger DHT blocker) outperformed both, but Finasteride's safety profile wins for most.
- US Stat: NIH data shows 80% adherence yields 70% improvement rates.
Citations: PMC Study on Combo Therapy; Frontiers Review
Side Effects Compared: Safety Profiles of Minoxidil and Finasteride
Safety is paramount, especially with FDA oversight. Minoxidil's topical nature limits systemic issues: common complaints include scalp irritation (7-10% of users), per Mayo Clinic. Rare cardiovascular effects occur with oral low-dose versions.
Finasteride's oral absorption raises concerns: 2-4% report sexual dysfunction (libido, erectile issues), though a 2025 EMA update confirmed rare suicidal ideation links. The FDA issued alerts on compounded topicals in April 2025, urging branded Propecia use.
| Side Effect | Minoxidil | Finasteride |
|---|---|---|
| Sexual Dysfunction | Rare (<1%) | 2-4% |
| Scalp Irritation | 7-10% | None |
| Mood Changes | None | Rare (post-finasteride syndrome) |
Consult a US board-certified dermatologist via AAD resources for personalized risk assessment.
Internal link suggestion: Managing treatment side effects
Who Should Choose Minoxidil, Finasteride, or Both?
Minoxidil suits early-stage, diffuse loss in both genders—ideal for quick cosmetic boosts. Finasteride is best for men with DHT-driven recession, per Harvard Health. Women: Stick to Minoxidil; pregnant individuals avoid Finasteride entirely.
Rogaine for Women 5% Minoxidil Foam, Growth Treatment for Thinning & Hair Loss
Once-a-day unscented 5% minoxidil foam helps treat hereditary hair loss and thinning hair in women.
- Early Thinning: Start with Minoxidil for speed.
- Advanced Balding: Finasteride to halt progression.
- Maintenance: Combo for synergy.
A 2025 Cureus evaluation found 92% satisfaction with tailored approaches.
The Power of Combination Therapy: Minoxidil + Finasteride Results
Why settle for one when two amplify results? 2025 studies, including a PubMed meta-analysis, show combos boost density by 40-50% over solos. Topical Finasteride-Minoxidil sprays reduce systemic sides while enhancing efficacy.
In a JAAD trial, 79% achieved marked improvement vs. 41% on Minoxidil alone. FDA views this as safe for men; women can pair Minoxidil with spironolactone.
- Pro Tip: Use FDA-approved generics for cost savings—under $20/month via GoodRx.
Internal link suggestion: Top combo therapies reviewed
Practical Tips: Starting Your Hair Regrowth Journey
Step-by-step to success:
- Consult: See a dermatologist for diagnosis—rule out telogen effluvium or thyroid issues.
- Choose Form: Foam Minoxidil for sensitive scalps; oral Finasteride for convenience.
- Track Progress: Photos every 4 weeks; apps like Hair Track help.
- Lifestyle Boost: Biotin-rich diet, stress management per NIH recs.
Biotin 10000mcg and Collagen Supplement - Hair Growth Vitamins
High-potency biotin capsules with collagen promote hair growth and thickness for men and women.
US availability: Minoxidil at Walmart/CVS; Finasteride via Hims or dermatologist scripts.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Can I use Minoxidil and Finasteride together? Yes—2025 studies confirm enhanced results with minimal added risk.
Does Minoxidil work for receding hairlines? Moderately; better for crown. Pair with Finasteride for fronts.
What if Finasteride causes side effects? Switch to topical; discuss dutasteride with your doctor.
Is generic Minoxidil as effective? Absolutely—FDA-equivalent.
How long until I see results? Minoxidil: 2-4 months; Finasteride: 3-6 months.
Conclusion: Your Path to Thicker Hair Starts Here
In 2025, Minoxidil offers faster initial regrowth, while Finasteride provides robust DHT control. For optimal outcomes, consider their synergy backed by cutting-edge research. Remember, hair restoration is a marathon—patience and professional guidance yield the thickest rewards. Ready to act? Schedule a virtual consult with an AAD dermatologist today.
Internal link suggestion: Take our free hair loss quiz